Elastopor and Autofroth
Rigid Polyurethane (PUR) Foams
Aerospace engineers and design professionals are looking beyond traditional solutions to meet more critical energy, performance, environmental and cost-saving demands. Many are finding exceptional success using materials made with BASF’s Elastopor and Autofroth rigid polyurethane foams. One approach is to replace relatively heavy metal structures with thinner metal/polymer composite structures based on rigid foam reinforcements.
Thoroughly field proven, BASF rigid polyurethane foams have a closed-cell structure which provides superior insulation performance as well as structural and design enhancing physical properties. They are available with zero ozone depleting technology, using blowing agents approved by EPA’s SNAP program.
|
Features
|
Aerospace applications
BASF rigid polyurethane foam can be molded to a wide range of shapes, sizes, and densities offering innovative design possibilities. It can be easily painted, stained, laminated or foamedin-place for reduced material waste, fewer skilled labor requirements and improved productivity in manufacturing. They adhere well to a wide range of substrates, eliminating the need for adhesives and it provides reinforcing strength to other materials as part of a multilayer construction, void fill or other composite structure.
|
Structural foam
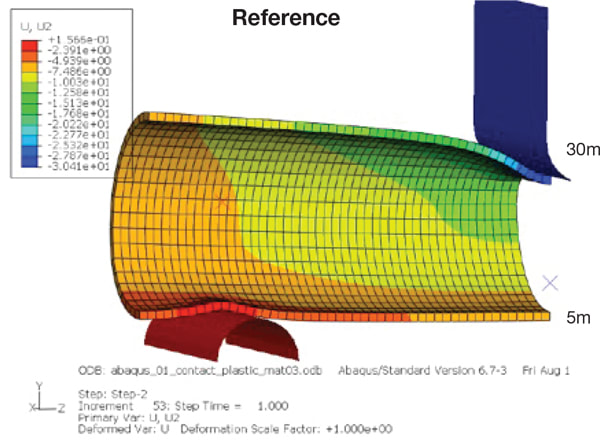
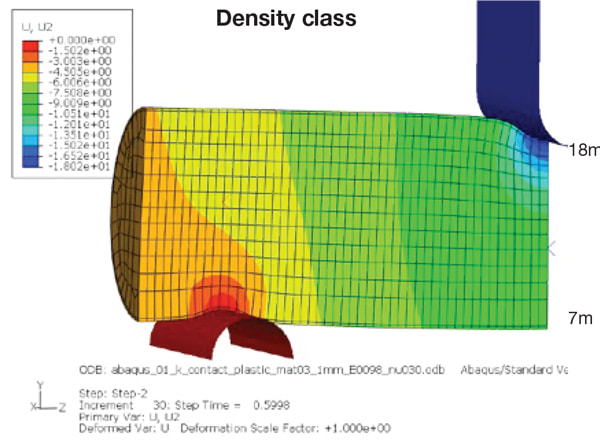
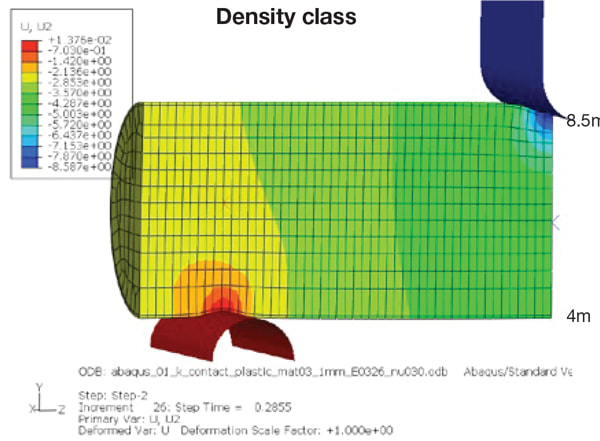
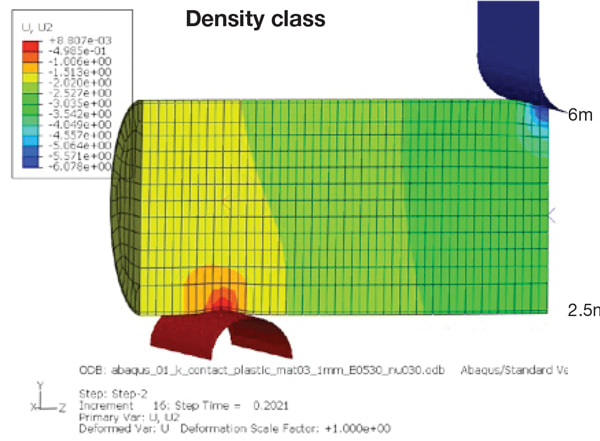
Structural foams are specially formulated to reduce weight by down-gauging metal wall thickness and reinforcing the structure. The rigid polyurethane foam improves strength and stiffness while reducing overall weight by as much as 50%. In one example, a tubular steel part is reduced from 3 mm to 1 mm wall thickness, filled with a 13 lb/ft3 structural foam and tested for deformation on a 3 point bend apparatus using a 30 kN load. The thinner walled (50% lower mass) part with the structural foam deforms only 18 mm compared to 30 mm for the thicker walled heavier part.
Comparison of deformation at 30 kN load
|
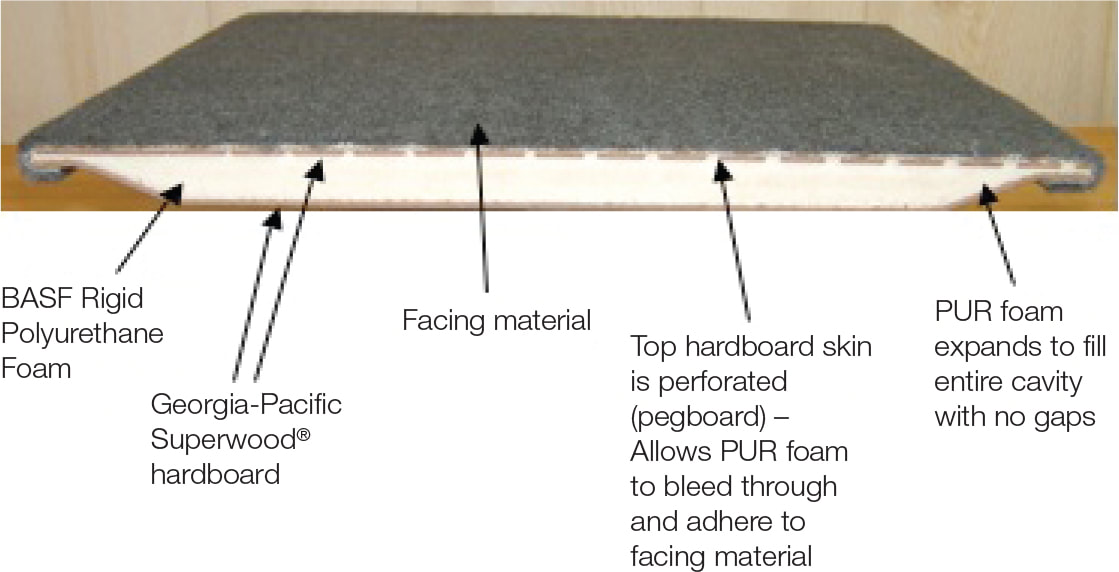
Composite load floors
Composite load floors or other structural panels are
lightweight and maintain a high level of stiffness across a wide temperature range. The composite typically consists of a polyurethane rigid foam core, hardboard (or other fiber based substrate) skins and a facing material. The entire composite, including facing material, is produced in a single step using a single mold. A wide variety of low flammability substrates and facing materials can be used with this technology to meet the specific needs of the aerospace industry. |